Understanding Precision Die Cutting
What is Precision Die Cutting?
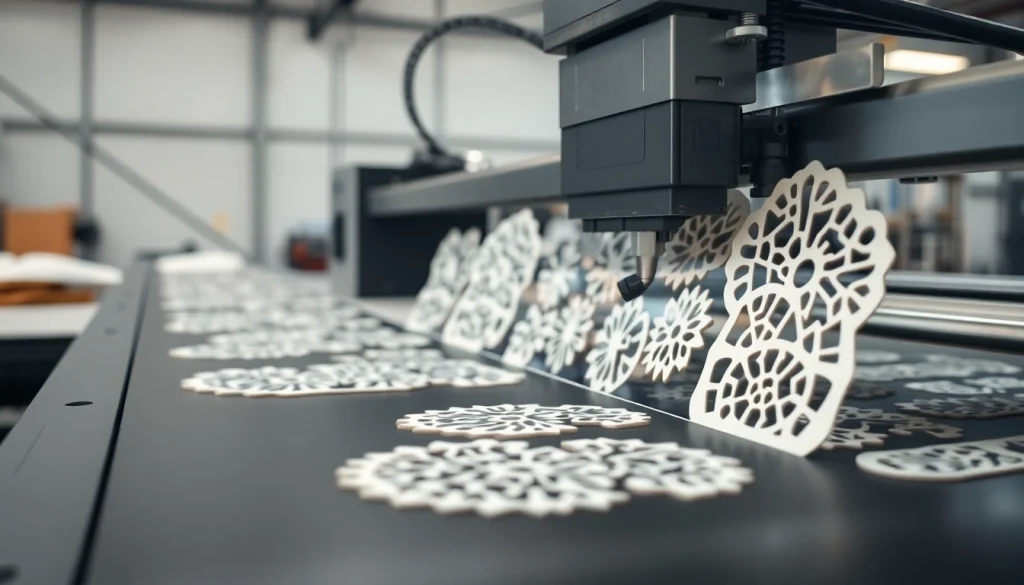
Precision die cutting is a highly specialized manufacturing process used to transform sheets or rolls of material into custom shapes and sizes using sharp metal dies. This technique ensures precision and uniformity, making it an ideal choice for industries requiring intricate designs and dimensions. During the process, the die cuts through the material at a specified pressure and speed, allowing for the production of intricate shapes, patterns, and components with tight tolerances. The precision die cutting method is especially sought after in sectors such as packaging, automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
Key Benefits of Precision Die Cutting
The advantages of precision die cutting are numerous and impactful across various industries:
- High Accuracy: Achieves precise cuts and shapes with minimal tolerances, crucial for complex designs.
- Efficiency: Capable of producing large volumes of parts quickly, thus reducing lead times significantly.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While initial setup costs can be high, the long-term savings on labor and material waste often justify the expense.
- Versatility: Effective on a wide range of materials, including paper, plastic, fabric, foam, and metal.
- Consistency: Ensures that every part produced is identical in shape and size, critical for assembly processes.
Common Applications Across Industries
Precision die cutting is applied in multiple sectors, each benefiting from its unique capabilities:
- Packaging: It creates custom boxes, labels, and displays tailored to brands and products.
- Automotive: Often used to produce gaskets, insulation pads, and prior components, ensuring they fit perfectly.
- Electronics: Essential in fabricating items such as insulation sleeves and insulating parts used in electrical systems.
- Medical Devices: Provides precise cutouts for flexible materials used in various types of medical supplies and devices.
The Process of Precision Die Cutting
Materials Used in Precision Die Cutting
The selection of material plays a significant role in the die cutting process. Common materials include:
- Paper and Cardboard: Widely used for packaging and artistic projects.
- Plastic Films: Used in packaging, electronics, and medical applications due to their durability and flexibility.
- Foam: Commonly required in applications needing cushioning and insulation properties.
- Thin Metals: Utilized in manufacturing electronic components and specialized tools.
Step-by-Step Workflow Explained
The die cutting process can be broken down into several key steps:
- Design: CAD software is used to create a detailed design of the item to be die cut.
- Die Creation: A specialized die is crafted from materials capable of cutting through the chosen base material.
- Setup: The die is mounted on the cutting machine, ensuring proper alignment and functionality.
- Cutting: The machine cuts the material using the die, which can either be a rotary or flatbed system, depending on the design requirements.
- Quality Check: Each batch is inspected for precision and quality, ensuring adherence to specifications.
- Final Processing: Additional treatments such as folding, gluing, or printing can be added after cutting.
Technology Innovations in Precision Processes
Advancements in technology continue to enhance the efficiency and capabilities of precision die cutting:
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC): Enhances precision and allows for customization of complex designs quickly.
- Laser Die Cutting: Provides high levels of accuracy and is ideal for intricate or detailed designs.
- Automation: Reduces manual intervention, speeding up the process and minimizing human error.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implements systems for immediate feedback and adjustments, ensuring optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Precision Die Cutting Service
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Vendor
Selecting the appropriate die cutting service provider is critical for ensuring quality and efficiency. Consider these factors:
- Experience: Look for vendors with proven expertise and a portfolio of completed projects relevant to your needs.
- Capabilities: Ensure they can handle the specific materials and types of die cutting you require—like rotary or flatbed systems.
- Quality Control: Investigate the procedures they have in place to guarantee high-quality output.
- Turnaround Time: Assess their ability to meet your deadlines, which is crucial for your production schedule.
- Customer Service: Choose vendors who have strong communication practices and are willing to collaborate closely with you.
Questions to Ask Your Die Cutting Partner
Before finalizing a provider, consider asking these essential questions:
- What types of materials do you work with?
- Can you provide references or case studies from previous clients?
- What is your standard delivery time for projects?
- How do you ensure precision and quality throughout the production process?
- What technologies do you employ for die cutting?
Evaluating Cost vs. Quality
Balancing cost and quality often requires careful consideration. It’s essential to ascertain that:
- You’re not compromising on quality for the sake of lower costs—this could lead to inefficiencies or product defects.
- Long-term partnerships can sometimes offer better pricing without sacrificing quality as opposed to one-off projects.
- Identify cost drivers such as the complexity of the design and material types to understand better where your budget is allocated.
Challenges in Precision Die Cutting
Managing Tolerances and Specifications
Precision die cutting inherently comes with challenges, especially in managing tolerances:
- Understanding Tolerance Limits: Getting familiar with the tolerance limits specific to your materials and applications is crucial.
- Consistency: Maintaining consistent quality across various production runs can be challenging but is essential for quality assurance.
- Adjustments During Production: Understanding how to make quick adjustments when issues arise is equally important.
Common Problems and Their Solutions
Like any manufacturing process, die cutting can present obstacles:
- Material Misalignment: Can lead to inconsistent cuts; always ensure proper setup and calibration before cutting.
- Tool Wear: Regular inspections and maintenance of cutting tools can prevent premature wear and maintain cut quality.
- Material Variance: Variations in material quality can affect outcomes; sourcing high-quality materials from reliable suppliers is vital.
Maximizing Efficiency While Reducing Waste
Operators should make continual efforts to enhance efficiency:
- Optimize Layouts: Design layouts to maximize material use and minimize waste during the cutting process.
- Production Planning: Schedule runs appropriately to reduce downtime between jobs, ensuring higher output.
- Staff Training: Investing in employee training can lead to better handling of machinery and immediate troubleshooting.
Future Trends in Precision Die Cutting
Emerging Technologies and Materials
As the industry progresses, several trends are impacting precision die cutting:
- 3D Printing Integration: Utilizing 3D printed dies could shift the landscape by offering more complex designs without the traditional setup times.
- High Speed and Automation: The push toward automation will continue to shape operational efficiencies and lower costs.
- Sustainable Materials: As eco-consciousness rises, the industry will increasingly look to sustainable and recyclable materials.
Predictions for Industry Growth
The precision die cutting market is expected to see significant growth, driven by:
- Increasing demand from the packaging industry for customized solutions.
- Technological advancements facilitating a more streamlined production process.
- Expansion of applications in automotive and medical sectors due to the need for high-precision components.
How to Stay Competitive in the Market
To remain competitive, businesses should consider:
- Innovation: Consistently explore new technologies and methodologies to stay ahead.
- Customer Engagement: Maintain communication with clients to understand their evolving needs and adapt offerings accordingly.
- Continuous Improvement: Implement Lean or Six Sigma strategies to constantly improve operational efficiencies and reduce waste.